Image Companding and Inverse Halftoning using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
This paper presents a deep learning technology for tackling two traditional low-level image processing problems, companding and inverse halftoning. This paper makes two main contributions. First, to the best knowledge of the authors, this is the first work that has successfully developed deep learning based solutions to these two traditional low-level image processing problems. As well as introducing new methods to solving well-known image processing problems, this paper also contributes to a growing literature that demonstrates the power of deep learning in solving traditional signal processing problems. Second, building on insights into the properties of visual quality of images and the internal representation properties of a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) and inspired by recent success of deep learning in other image processing applications, this paper has developed an effective deep learning method that trains a deep CNN as a nonlinear transformation function to map a lower bit depth image to higher bit depth or from a halftone image to a continuous tone image, and at the same time employs another pretrained deep CNN as a feature extractor to derive visually important features to construct the objective function for the training of the transformation CNN. Extensive experimental results are presented to show that the new deep learning based solution significantly outperforms previous methods and achieves new state-of-the-art results.
Overview
We take full advantage of the convolutional neural networks both in the nonlinear mapping functions and in the neural networks loss functions for low-level image processing problems. We not only use a deep CNN as a nonlinear transformation function to map a low bit depth image to a higher bit depth image or from a halftone image to a continuous tone image, but also employ another pre-trained deep CNN as a feature extractor or convolutional spatial filter to derive visually important features to construct the objective function for the training of the transformation neural network. Through these two low-level image processing case studies, we demonstrate that a properly trained deep CNN can capture the spatial correlations of pixels in a local region and other visually important information, which can be used to help a deep CNN to infer the "correct" values of pixels and their neighbors. Our work further demonstrates that halftone images and heavily compressed low bit depth images, even though showing visually annoying artifacts, they have preserved the overall structures of the images which are sufficient to enable deep neural networks to recover the original signals to a high degree of fidelity.
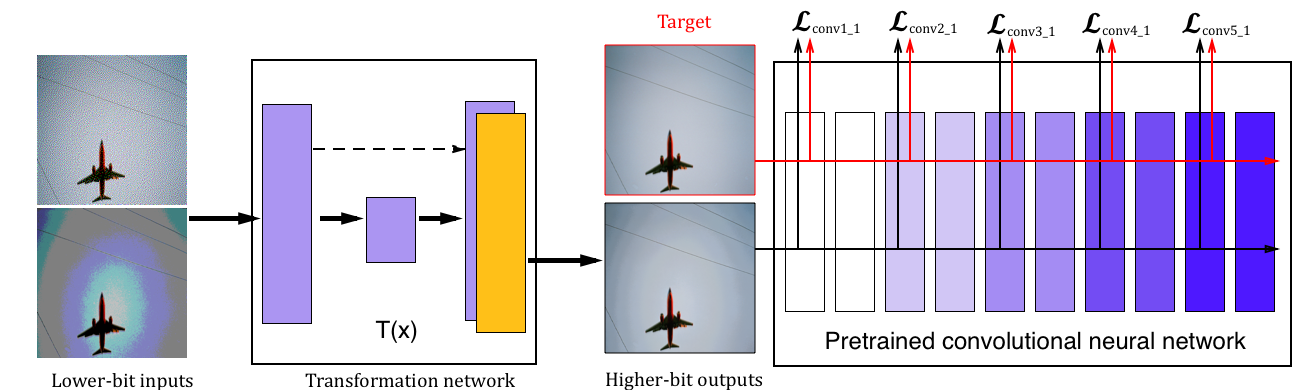
Results
We perform experiments on two image processing problems: image companding and inverse halftoning. Our results are denoted as CNN Inverse.
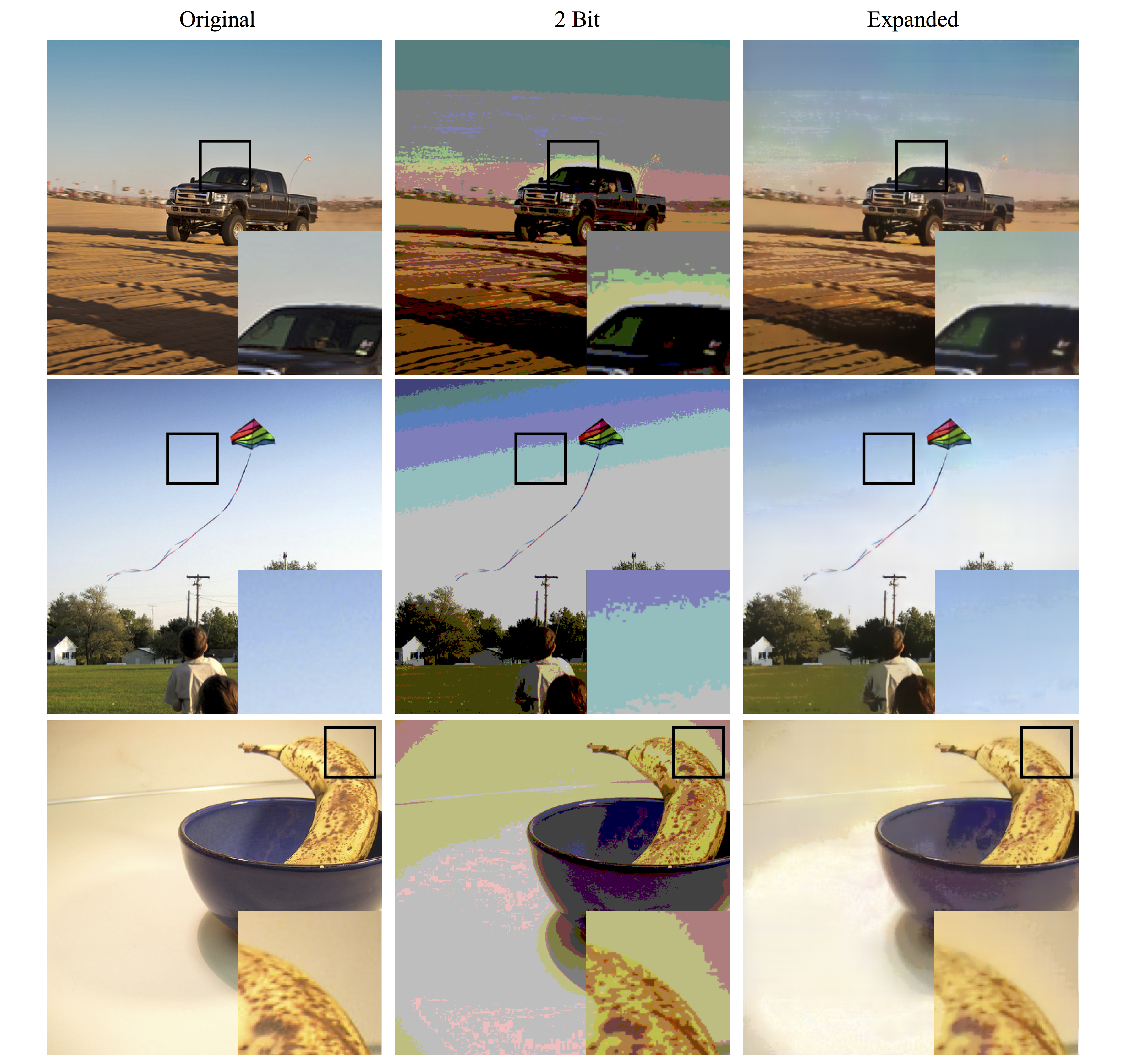
Color Images
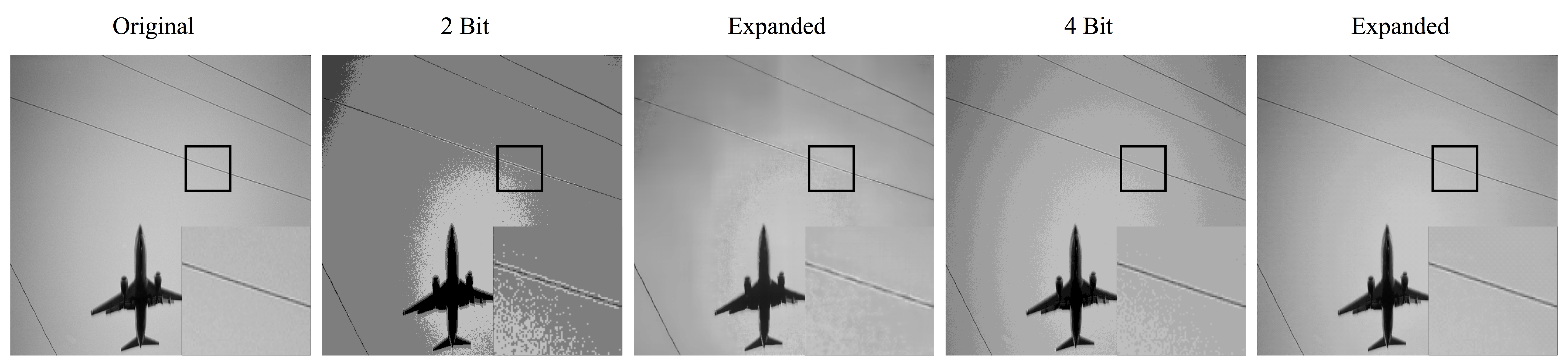
Grayscale Images
Color Images
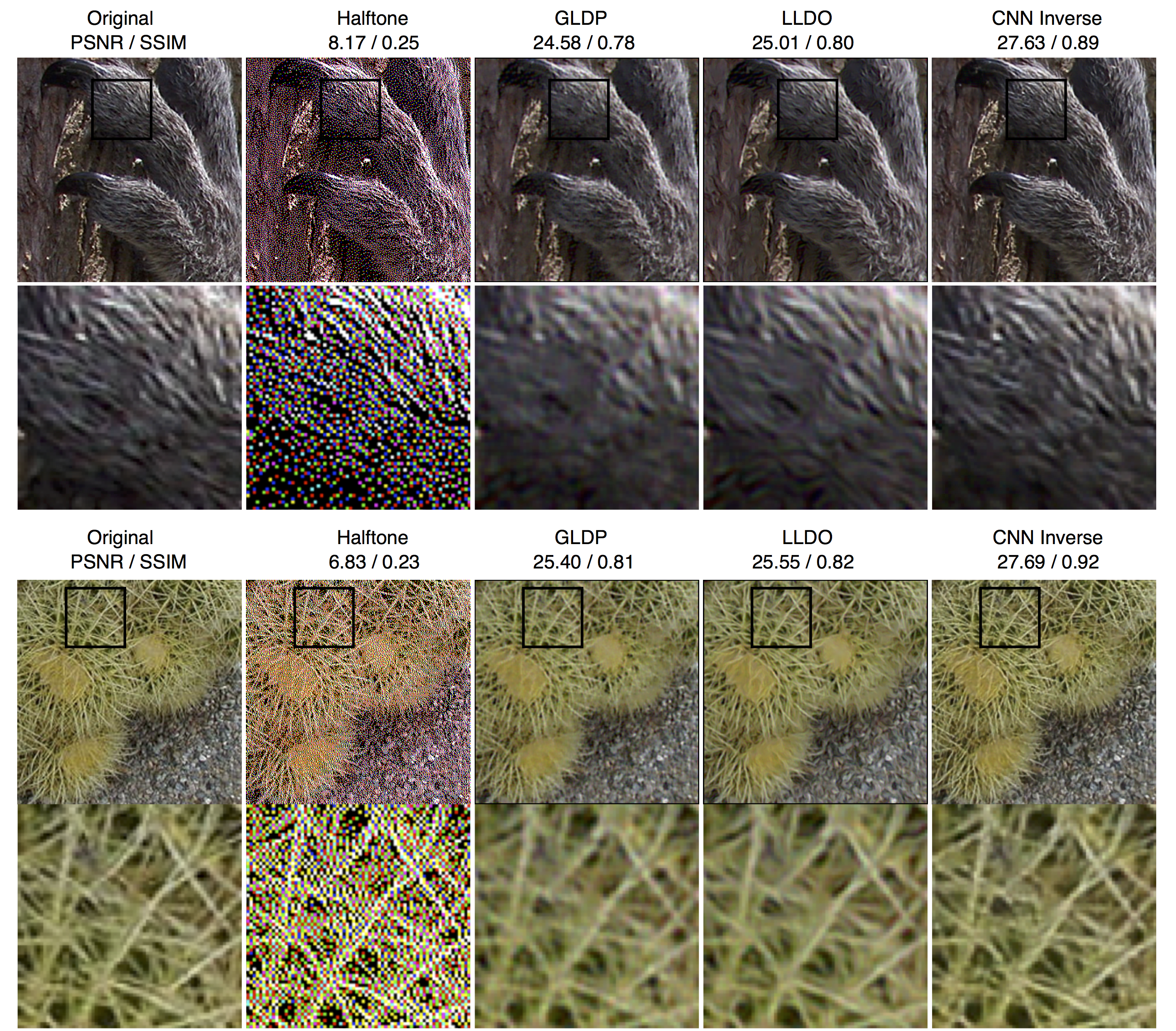
Grayscale Images
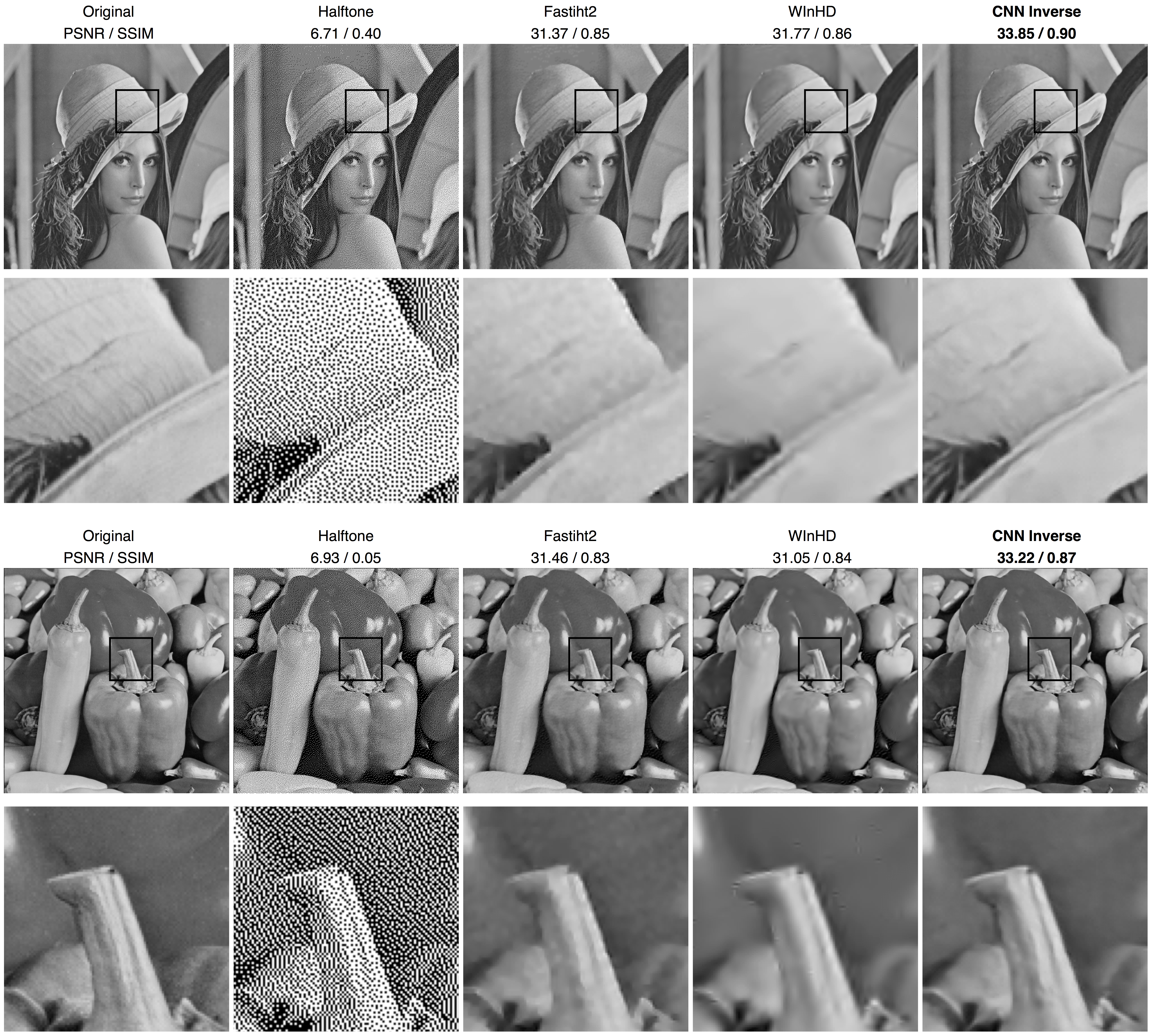
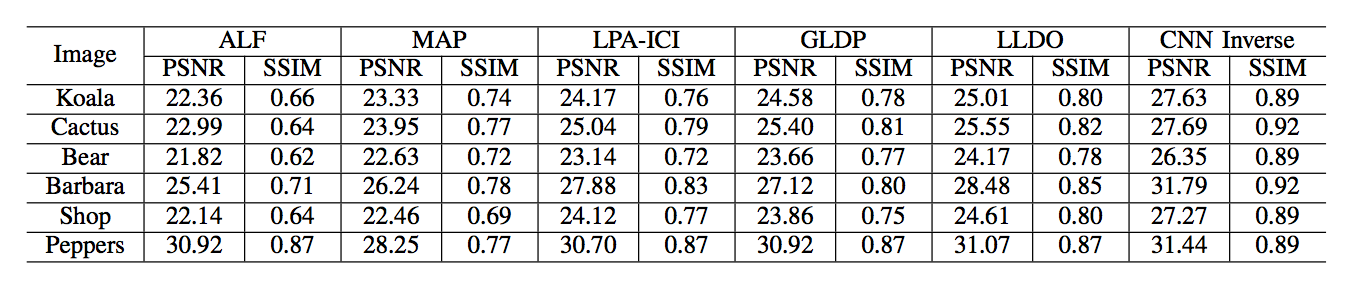
Quantitative Evaluation
We compare our method (CNN Inverse) with different inverse halftoning methods based on PSNR (dB) and SSIM measurement.